2364
Argentine President Cristina Fernández de Kirchner is currently battling allegations of corruption, and when Argentina’s Supreme Court upheld in October a media law that takes on press monopolies while promoting diversity in media ownership, journalists in the English-speaking North covered it as a blow to press freedom.
The Audiovisual Services Act, originally introduced by Kirchner in 2009, replaced the Radio Broadcasting Law of 1980, put in place by the military regime that ruled the country from 1976 to 1983. The junta used the 1980 law, which promoted the corporatization of news information, to speed up the privatization and monopolization of media in Argentina after independently reported stories undermined military rule, according to the Argentine Information Secretariat's 1981 report, Argentine Radio: Over 60 Years on the Air
Although the return of constitutional rule in 1983 granted journalists more political freedoms, it largely ignored economic ones. Even after the collapse of the military dictatorship, the 1980 law allowed wealthy business owners, many of whom had been sympathetic to the regime and its pro-market stance, to dominate journalism in Argentina.
Clarín, founded in 1945 and today one of Argentina’s most recognized daily newspapers, fared well throughout the junta’s administration, eventually surpassing the sales of its main competitor, Papel Prensa. In 1999, the newspaper’s publisher reorganized itself as Grupo Clarín, managing to acquire over 200 newspapers and several cable systems across the country to become Argentina's largest corporate media organization (Reuters, 10/32912). The organization currently has a market share of 47 percent and holds 158 licenses (Financial Times, 10/29/2013).
2365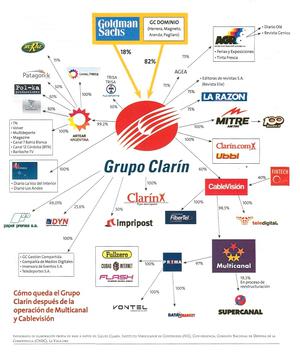
The Kirchner-backed media law places limits on the size of media conglomerates in an attempt to diversify ownership of news distribution: media companies will now be limited to a maximum of 35 percent of overall market share. The new law also imposes a national limit of 24 broadcast licenses per company, meaning the group will have to sell off dozens of operating licenses or have them auctioned by the state (Christian Science Monitor, 10/30/13).
Many Western reporters covering Argentina, however, dismiss the danger of concentrated corporate control of journalism, instead focusing on the perceived danger that government regulation of media could silence political opposition—echoing claims made by Grupo Clarín and other private conservative organizations.
U.S. news stories covering the Supreme Court's decision to uphold the media law tended to read like press releases for Grupo Clarín, leading with the consequences it will have on the monolithic media conglomerate. That angle was an easy sell to corporate news outlets that have an interest in focusing on governmental limits on journalism without discussing the problems of a privatized, highly concentrated news market.
The Washington Post (11/1/13), for example, headlined its editorial on the topic “In Argentina, a Newspaper Under Siege," presenting Grupo Clarín as the victim of a governmental attempt to silence opposition. “Sadly, however, Ms. Fernández and her cronies still pose a threat to the country's democratic institutions,” the Post wrote:
That became clear Tuesday, when the Argentine Supreme Court, under heavy pressure from the president's office, upheld a law aimed at destroying one of South America's most important media firms, Grupo Clarín.
The company operates one of Argentina's biggest newspapers, called Clarín, which has been one of the few media outlets to challenge Ms. Fernández's policies. The law would force the company to auction off cable television and Internet businesses that provide most of its revenue, thus reducing potential funding for Clarín's newsroom.
The article victimizes Grupo Clarín, giving readers the impression the Argentine government established the limits with the intentions of “destroying” the group. Yet the Post fails to mention that the United States also has a history of issuing similar outlet restrictions, like the Telecommunications Act of 1996 that placed a 35 percent limit on market ownership. Although the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) raised that limit to 45 percent in 2003 during a private reevaluation, the agency still has the power to regulate media ownership.
The Post editorial board also linked the media law to Kirchner's attempts to nationalize major companies in other industries, including travel and energy, saying that she and her late husband, whom she succeeded as president, have sought to "concentrate power in their own hands."
The Wall Street Journal (11/5/13) chimed in:
In the past few years, the government has shifted nearly all its public advertising money to media outlets that provide it with positive coverage—a move the Supreme Court has condemned, to little effect… Leading newspapers like Clarín and La Nación also say they are suffering from an ad boycott orchestrated by the government—an allegation the government denies.
The Journal ignores the fact that the Kirchner administration continues to direct public advertising to smaller conservative media groups within the Association of Argentine Journalism (CITE); diversified media ownership, rather than ideology or partisan affiliation, is the criterion for government subsidy. Despite the fact that there is an alleged “ad boycott orchestrated by the government,” both Grupo Clarín and La Nación continue to receive more revenue from private advertisers than any other media outlet in Argentina, according to a 2011 report published by the Comisión Nacional de Comunicaciones.
The Associated Press (11/4/13), reporting on Grupo Clarín's recent decision to break itself up into six parts in order to comply with the law, presented the legislation as little more than a politically motivated attack on one corporation:
The licenses are essential to Clarin's cable television networks, and synergy between the finances and news content of the group's TV and radio stations, websites and newspaper are key to its power. Many government supporters want nothing less than Clarín's defenestration as a viable opponent.
The Associated Press's framing in the aforementioned article takes the side of Grupo Clarín: They write that Clarín’s unregulated licenses are “key to its power” without airing arguments against the corporate consolidation of public news information. They also make the assumption that Kirchner constituents “want nothing less than Clarín's defenestration” without providing quotes from pro-media regulation activists in Argentina aside from government officials.
And the Miami Herald (10/23/13) published a column by Roger Noriega of the American Enterprise Institute, formerly of the George W. Bush State Department. Noriega argued that the law was aimed at "silencing the independent media" and that nothing less than "the fate of the free press" was at issue. "Of course, it is all too predictable that these divested media licenses will fall into the hands of compliant Kirchner cronies," wrote Noriega. "This transparent tactic is lifted from the playbook of leftist caudillos in Venezuela, Ecuador, Bolivia and elsewhere." 2366
A quick sift through Noriega’s column reveals that his definition of "independent media" elides the dependency that media organizations like Grupo Clarín and La Nación have on funding from private corporations that have personal profit-making agendas—a dependency that forces both groups to embrace the political ideologies of their sponsors in order to maintain steady revenue. A truly "independent media" would be free of both government and corporate domination. It is also evident that his notions of a "free press" are founded upon free-market, neoliberal principles, championing corporate domination of political news coverage. His tactic of utilizing the term "free press" in correlation with unregulated, monopolized, and corporatized news media seems to hail straight from the playbook of McCarthyist lexicon, to borrow a few words from his comparison.
Overall, corporate journalistic monopolization and the concentration of news media is more of a threat to press freedom in Argentina than government regulation is. The domination of public discourse by media groups with private, corporate interests is dangerous to readers who are oftentimes unaware of the advertising revenue models of organizations like Grupo Clarín; in its obligations to maximize profits, it has strategic incentive to promote the interests of its commerical sponsors rather than the people of Argentina searching for objective news coverage.
Many Western journalists have painted Kirchner as an authoritarian leader desperate for control over news coverage in order to maintain a positive image, without realizing that in modern times, media ownership is just as influential as government suppression of speech. While many conservative Argentines have blindly sided with groups like Grupo Clarín in criticizing the government’s large advertising presence in news organizations that are friendly with the incumbent administration, they have failed to recognize that there is a difference in advertising intentions and content between the Kirchner administration and private corporations: the former publicizes information about social welfare programs available to citizens, while the latter promotes products whose profits benefit the small percentage of Argentines who have seemingly little at stake in quality social programming.
The Supreme Court of Argentina and the Kirchner administration have recognized that progressive interpretations of freedom of speech include democratic and popular control over mass information and national discourse. They have also recognized the need for public diversity in media ownership that fosters economic freedoms within journalism, allowing any citizen, regardless of ideology and economic background, to have just as amplified of an opinion as a corporate news organization does—all without violating political rights.
Organizations that have claimed otherwise, or that echo the cries of victimization made by Grupo Clarín, fail to analyze alternative qualities of freedom of speech.
Ramiro S. Fúnez is a Honduran-American political journalist and activist earning his master's degree in politics at New York University. Follow him on Twitter at @RamiroSFunez.

